Harnessing the Hidden Energy: Unraveling the Secrets of Sewer Systems
In the bustling cities around the world, there exists a remarkable, yet often overlooked, infrastructure that plays a crucial role in our daily lives - sewer systems. These underground networks, similar to the subway, have a rich history in both Europe and the United States.
Beyond their primary function of managing waste, sewer systems hold an intriguing potential for energy conservation. Some of the water flowing through these pipes retains energy, particularly the heat from hot water used in our everyday lives. Although this is not a massive energy source, this waste heat can be effectively utilized to contribute to our energy needs.
Utilizing Sewer Heat for Efficient Road Heating
Uncovering the untapped potential of sewer systems can lead to a more sustainable future.
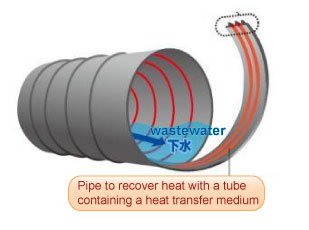
In urban infrastructure, an innovative approach utilizes the heat energy from domestic wastewater in sewer pipes. This technique involves heat pipes to transfer the accumulated heat from underground sewer pipes to structures like roads.
In regions experiencing snowfall, road heating is employed during winter months to warm the road surface, reducing snow accumulation and minimizing labor-intensive snow removal efforts. In areas with heavy snowfall, road heating becomes an essential solution, preventing snow buildup by melting it directly on the road surface.
Efforts are underway to optimize energy usage and curb costs by harnessing sewer heat as an energy source. This energy exchange not only heats the road surface but also leads to significant energy savings. This ingenious application of sewer heat exemplifies how modern urban infrastructure efficiently combines existing resources for enhanced sustainability.
Snow in the Niigata Prefecture
Leveraging Sewer Heat for Road Heating in Niigata Prefecture
Niigata Prefecture is situated on the Sea of Japan, popular for its scenic mountains and beautiful rice fields.
The area is renowned for heavy snowfall averaging over 4 meters per season, experiences temperatures ranging from -5°C to 5°C on many days, with daytime snow melting.
This unique climate presents an intriguing opportunity for road heating using sewer heat. Though sewer heat alone may not qualify as a substantial energy source, employing heat pipes to release this stored warmth to the road surface proves to be a viable solution. The low energy requirements make road heating feasible in this region.
Urbanization, especially in areas like Niigata City, has expanded sewer networks throughout the city. Aims to harness the heat energy from these sewers for efficient snow melting seem promising.
By capitalizing on sewer heat's hidden potential, Niigata Prefecture could revolutionize its snow management practices and set an example for other snowy areas worldwide. In this journey towards a greener and more resourceful future, the harmony between technology and the environment takes center stage.
Unveiling the Hidden Potential of Sewer Heat
The concept of sewer heat was relatively unknown until recently, yet in Japan, groundwater has long been used to provide warm water in winter and cold water in summer. Sewer heat serves as a prime example of harnessing this age-old wisdom.
Consider this: a significant portion of wastewater in sewage pipes carries thermal energy, like the warmth from bathtub water. Until now, this valuable heat was merely discarded. However, a new approach has emerged in Niigata Prefecture, where the sewer network is utilized for snow-melting facilities and other practical purposes, albeit on a regional scale.
As we further explore the possibilities, it's fascinating to contemplate the potential for other creative applications of sewer heat. This untapped resource holds the promise of innovative solutions that could benefit communities far and wide. From contributing to energy conservation to fostering sustainable practices, sewer heat exemplifies how established systems can evolve to meet modern challenges. As we continue delving into the realm of urban infrastructure and its interaction with the environment, the potential for ingenious solutions remains boundless.